Introducing Potter Pi
Introduction
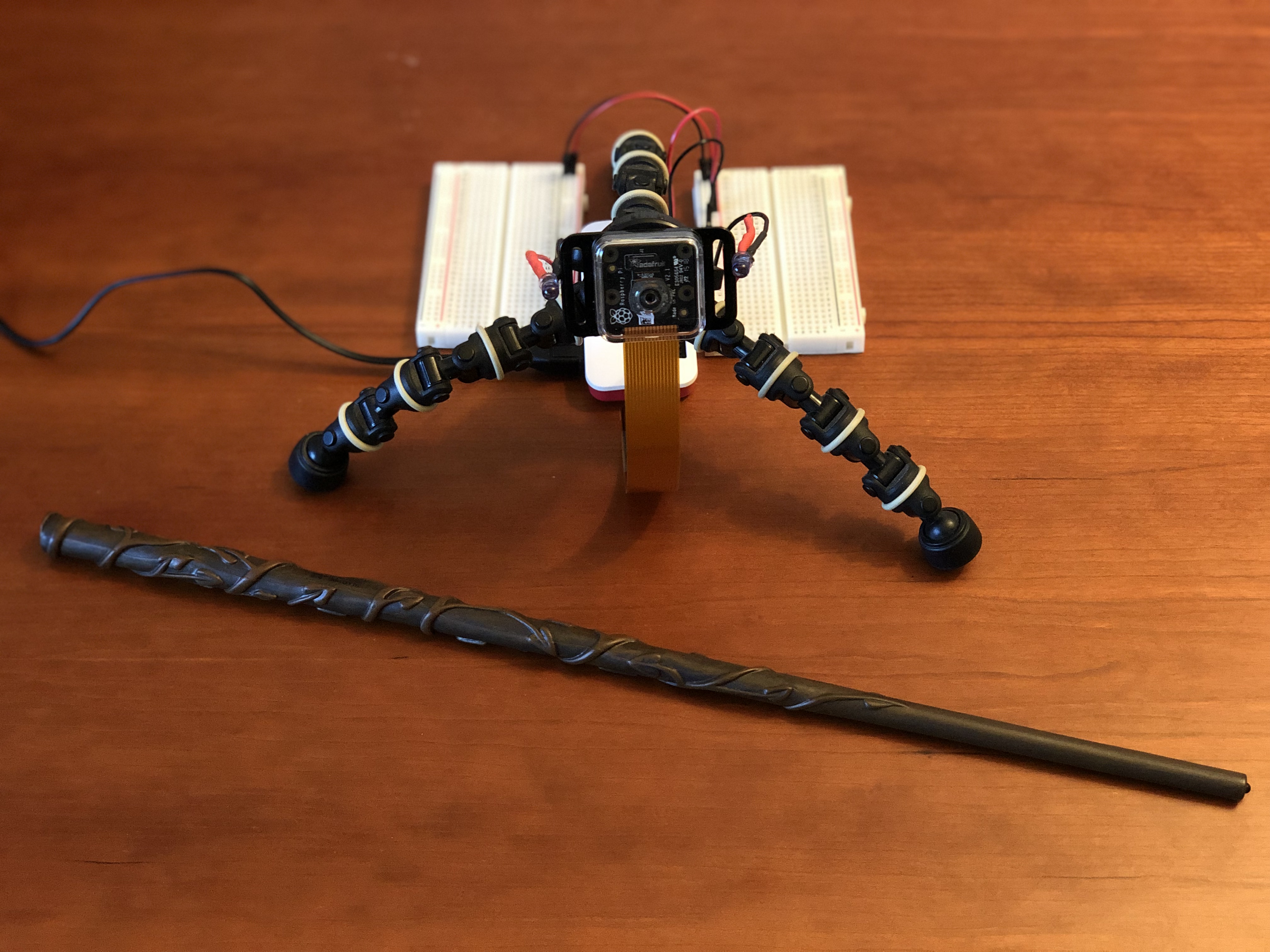

Several months ago, my brother gifted me a wand after visiting the Wizarding World of Harry Potter. Not wanting it to go to waste, I decided to make something with it. After some googling, I ran into a couple open source projects, which inspired me to create my own DIY Harry Potter wand detection & spellcasting system.
Check out this YouTube playlist to see it in action. The playlist shows the project's evolution in reverse order. It's pretty neat to see where it is now and where it first started.
How it works
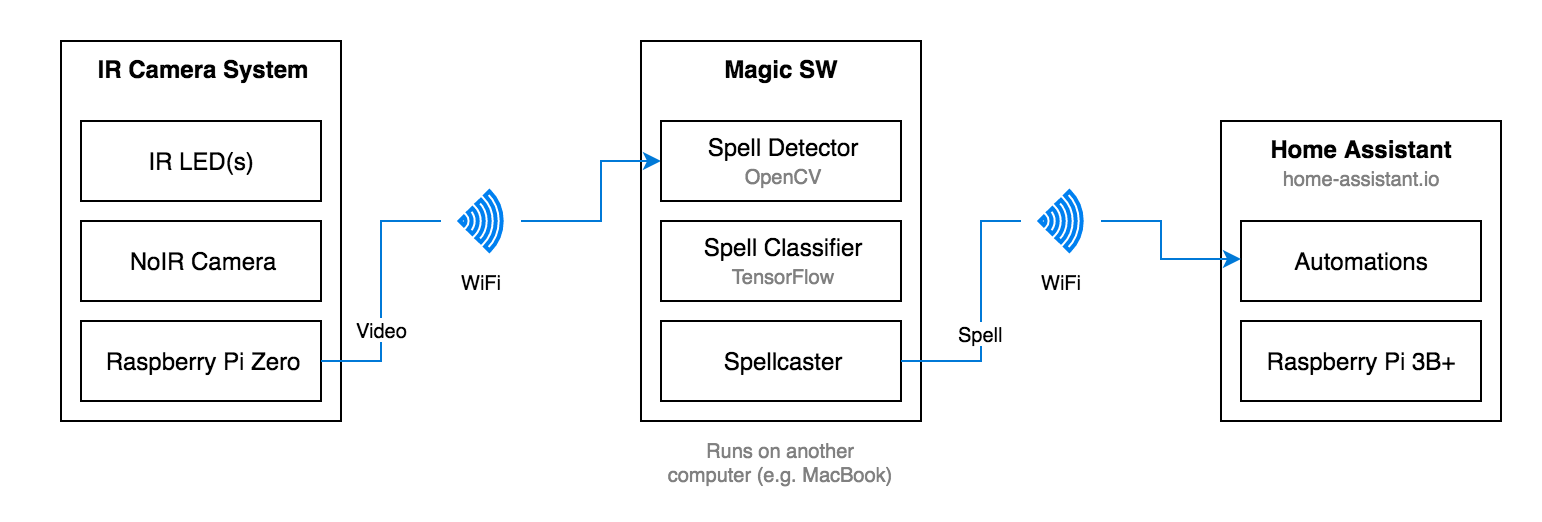
IR Camera System
The IR Camera System consists of a Raspberry Pi Zero, a NoIR camera and two IR LEDs. When the wand tip is in view, the emitted IR light is reflected back to the camera. The video is then streamed over WiFi so that another computer can receive the video feed, track the wand, classify and detect spells.
Magic Software
The Magic Software processes the video stream using OpenCV to isolate the illuminated wand tip from the rest of the frame. The wand pattern is then sent to a Spell Classifier, which uses TensorFlow to determine the spell. The Spellcaster triggers the spells using the Home Assistant REST API to turn on / off lights, say hidden messages, and so on.
The software can detect three spells and can be easily extended to add more:
| Spell | Wand Pattern |
|---|---|
| Lumos |  |
| Nox |  |
| Revelio |  |
In theory, this can run on the Pi powering the IR Camera System, but you will get better performance on a standard computer. Plus, you can see the video output, which is helpful for testing and debugging purposes.
Home Assistant
Home Assistant is an open source home automation framework that runs on a local server (in this case, a different Raspberry Pi). You can organize all your smart devices and create rules for various automations. In this project, automations have been set up for each spell: Lumos, Nox, and Revelio. When a spell has been cast by the Magic Software, the appropriate automation is triggered.
The code
The source code is available on GitHub. Refer to the Wiki for full setup details.